D suprachiasmatic nucleus. An injury to the spinal cord is not possible below the.
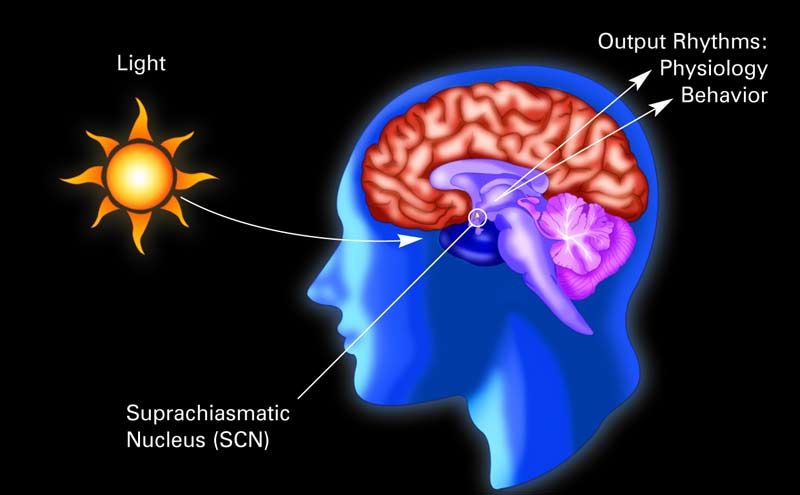
The tiny suprachiasmatic nucleus SCN of the hypothalamus plays a central role in the daily programming of organismic functions by regulating day-to-day oscillations of the internal milieu and synchronizing them to the changing cycles of day and night and of body state.

. A collection of 20000 neurons the suprachiasmatic nucleus SCN is the bodys master clock. This biological clock drives the daily expression of vital homeostatic functions as diverse as. What are the 3 primary brain vesicles that form from the neural tube.
Peripheral clocks dont need the brains master clock to function correctly. The researchers developed a new genetic mouse model by suppressing Bmal1 one of the master genes that drives circadian rhythms in the suprachiasmatic nucleus SCN which serves as the brains central clock regulator. Large polar molecules Carbon dioxide Glucose Lipid-based molecules.
In the human brain theres a master clock called the suprachiasmatic nucleus SCN which serves to keep the entire body on time. What functional brain system participates in memory learning emotion and behavior. B caudate nucleus.
Which of the following should not cross the blood-brain barrier with ease. Wedged deep within the brain two little wing-shaped nuggets of neurons called the suprachiasmatic nucleus serve as a master clock setting the daily schedule for the entire body. What part of the spinal cord carries motor information from the brain.
Which brain nucleus serves as the bodys master clock. For example light exposure tells it to produce less sleep-inducing melatonin. Forebrain midbrain hindbrain.
What are the 3 primary brain vesicles that form from the neural tube. The master biological clock that serves as the pacemaker for the bodys circadian rhythms is the suprachiasmatic nucleus SCN. Which brain nucleus serves as the bodys master clock.
The suprachiasmatic nucleus SCN serves as the bodys master circadian clock that adaptively coordinates changes in physiology and behaviour in anticipation of changing requirements throughout the 24-h day-night cycle 1-4. A small part of the brain called the suprachiasmatic nucleus serves as the bodys master clock receiving external light cues ideally from. Controls the motor activity on the left side of the body.
The brain s master clock is housed in the. New research further adds to our understanding of the circadian rhythm by suggesting that the suprachiasmaticus nucleus. It uses light as a signal.
The SCN sitting just above where the eyes nerves cross serves as a sort of atomic clock adjusting to the local light cycle and then synchronizing daily rhythms in the brain and body. Light-sensing cells in the retina transmit electrical impulses to the SCN which synchronizes the brain and body to the light-dark cycle. These pacemaker neurons recognize when sunbeams have slipped between your bedrooms blinds and they tell the clock genes and you that its time to rise.
D suprachiasmatic nucleus. THe neurotransmitter orexin plays a role in. The NT orexin plays a role in _____ the promotion of wakefulness.
If inputs and outputs from the suprachiasmatic nucleus SCN are severed its neurons. Its also sensitive to light. C pituitary gland.
The motor activity on the left side of the body. The SCN receives signals about the light-dark cycle through the visual system and passes that information along to another cell group in the hypothalamus known as the dorsomedial nucleus DMH. He describes in laymans terms how the brains superchiasmatic nucleus serves as the bodys master clock Operating through various genes in the brain the superchiasmatic nucleus takes cues from our external environment to synchronize the genes and circadian clocks that reside in and regulate the cyclical activity i n every cell in the body.
The researchers developed a new genetic mouse model by suppressing Bmal1 one of the master genes that drives circadian rhythms in the suprachiasmatic nucleus SCN which serves as the brains. The suprachiasmatic nucleus SCN a group of cells in the brains hypothalamus serves as the bodys primary biological clock. Which brain nucleus serves as the bodys master clock suprachiastmatic nucleus.
The master biological clock that serves as the pacemaker for the bodys circadian rhythms is the suprachiasmatic nucleus SCN. Diminished Bmal1 expression reduced the strength of the clock signals produced by the SCN by about 80. The suprachiasmatic nucleus SCN a group of cells in the brains hypothalamus serves as the bodys primary biological clock.
Forebrain midbrain hindbrain. A pineal gland. Which brain nucleus serves as the bodys master clock.
Inside Life Science How Our Bodies Keep Time Live Science

Circadian Rhythm Sleep Healthy Sleep

Central And Peripheral Clocks In Human Suprachiasmatic Nucleus Scn Download Scientific Diagram

0 Comments